Discription: This blog post explains the reaction of HCOOCH with CH₂ and H₂O in simple terms, covering the chemical process, resulting compounds, and its significance in real-world chemistry.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O is a chemical compound linked to formate esters and organic acids. It may act as a hydrated ester or reaction intermediate in chemical processes. This compound plays a role in making esters, breaking down molecules, and serving as a mild solvent. Related compounds such as methyl formate are used in eco-friendly products and biodegradable materials. HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O helps support cleaner production methods. Its structure allows easy interaction with other substances, making it valuable in labs and factories focused on safe, efficient, and sustainable chemical solutions.
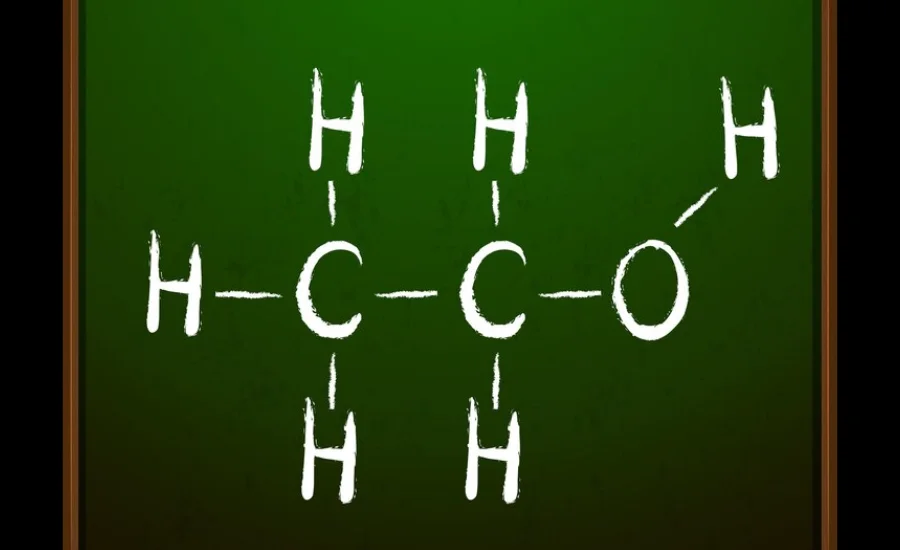
Chemical Composition and Structure
Molecular Formula Breakdown
HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O is linked to formate esters or organic acids. Here’s what each part means:
- HCOOCH: Likely represents a formate ester group. This group comes from formic acid (HCOOH) and plays a role in many chemical reactions.
- CH₂: Stands for a methylene (-CH₂-) group. It often acts as a bridge between other parts of the molecule.
- H₂O: Water might be part of the reaction or exist as a hydrated form of the compound.
Structural Representation
- The methylene (-CH₂-) group acts as a connector between molecules, affecting how stable and reactive the compound is.
- Water may be separate or help form bonds with esters.
Possible Stereochemistry Considerations
- Formate esters commonly do now not have chiral centers, so stereochemistry might not be extensive.
- If the compound reacts with other chemical substances, its spatial association may additionally have an effect on the response.
- The 3-dimensional structure should have an effect on how it interacts with different molecules.
Chemical Properties of HCOOCH CH2 H2O

Physical Properties
Molecular Weight: The molecular weight varies based on its exact structure. If it is a formate ester with water, its weight equals the sum of its atomic masses.
- Boiling and Melting Points:
- The boiling point is likely low since many formate esters are volatile.
- The melting point can vary, especially if water is involved in the structure.
- Density and Solubility:
- Density varies based on molecular structure and water interaction.
- It may be partially soluble in water, but it likely dissolves better in organic solvents like ethanol.
Chemical Behavior
- Acidity or Basicity:
- This compound is usually neutral or slightly acidic due to its formic acid origin.
- The presence of water may slightly change its pH.
- Reactivity with Other Compounds:
- Response with other connections:
- It can react with acids or bases and break into small molecules.
- It reacts to form new organic compounds through esterification.
- Stability in different situations:
- It stays stable at room temperature but may break down in strong acids or bases.
- Exposure to air or moisture can speed up chemical processes and reactions.
- If it is unstable, it should be stored in airtight containers to prevent evaporation.
Synthesis and Preparation
How It’s Made
- HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O is a hydrated organic compound.
- It is usually made using esterification, carbonylation, or hydrolysis.
- The process changes based on how the compound will be used.
Key Ingredients
- Formic acid (HCOOH): A major reactant in ester formation.
- An alcohol (methanol or ethanol): Helps create the ester.
- Water (H₂O): May be present in the reaction.
Reaction Conditions
- Temperature: The reaction generally occurs best within a moderate range of 50 to 80°C to support optimal chemical activity.
- Pressure: Some methods require moderate pressure for better yield.
By-Products
- Water: A common by-product of esterification.
- Other organic compounds: May form in small amounts based on reaction conditions.
Applications and Uses
Industrial Uses
- Solvents: Used in paints, coatings, and cleaning agents due to its fast evaporation.
- Adhesives: Helps improve the strength and durability of industrial adhesives.
- Pharmaceuticals: Acts as an intermediate in making certain medications and organic compounds.
Role in Biology and Environment
- Biodegradable: If it is a formate ester, it is able to wreck down into innocent substances in nature.
- Eco-Friendly: Some esters support green chemistry due to their low toxicity.
- Metabolism: Formate-primarily based compounds may additionally play a position in cell processes in living organisms.
Use in Organic Synthesis
- Intermediate Compound: Serves as a building block for more complex chemicals.
- Esterification: Helps produce new esters and alcohol derivatives.
- Catalysis: Used in chemical reactions to create biofuels and fine chemicals.
Safety and Handling
Health Risks
HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O may pose health risks. Breathing in its fumes can cause dizziness, nausea, or trouble breathing. If it enters the eye, it can cause irritation, water or discomfort. Swallowing the connection can be harmful and potentially cause digestive problems or toxicity. Appropriate safety conditions should always be followed when handling this drug.
Flammability and Environmental Impact
If this compound is a formate ester, it may be highly flammable and should be kept away from open flames, sparks, or heat sources. In case of a fire, appropriate extinguishing agents like dry chemical powder or carbon dioxide should be used. Environmentally, large spills could be harmful to aquatic life and contribute to air pollution if released in high quantities. However, some forms of this compound may naturally break down into less harmful substances over time.
Storage and Disposal
This chemical need to be stored in a fab, dry, and nicely-ventilated location. It ought to be stored in tightly sealed packing containers, faraway from strong acids, bases, or oxidizing dealers. Dispose of it safely. Instead, neighborhood dangerous waste disposal tips need to be followed, and it’s miles fine to apply authorized waste collection services for safe coping with.
Related Compounds and Derivatives

Similar Esters and Organic Acids
The connection HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O is probably related to esters and hydrated organic acids. Some common examples include methyl format and ethyl format (HCOOCH₃). These compounds evaporate quickly, dissolve in organic solvents and react easily in chemical processes.
How It Compares to Methyl Formate
It is regularly used as a solvent and a starting material in chemical synthesis. Compared to HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O, it does not comprise extra water molecules, that could imply HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O is a hydrated form or performs a function in water-associated reactions. This distinction could affect its balance, reactivity, and the way it behaves in specific environments.
Hydration and Hydrolysis Possibilities
HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O can interact with water through various reaction pathways.
- Hydrolysis: If mixed with water and a catalyst, it might break down into formic acid (HCOOH) and an alcohol.
- Hydration: Water could temporarily attach to the molecule, which might change its solubility and chemical properties.
- Decomposition: Under heat or strong chemicals, it might break down further, possibly releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other organic substances.
This makes the compound interesting for chemistry and industry, as its structure could influence how it reacts and what it can be used for. You may also like learning about the LG Gram Keyboard Ribbon Cable or exploring temperature data like 98.7, 87.8, 85.9, 90, 97.6 in chemical contexts.
Conclusion
HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O is a compound related to esters or organic acids, which play an important role in chemical synthesis and industrial applications. It can participate in estrification, hydrolysis and solvent reactions, making it useful in solvents, glue and drugs. The properties depend on the structure, reaction and environmentalability. Proper handling, storage and disposal are important due to potential health and fire risk. Compared to related esters such as methyl format, it can show unique hydration or hydrolysis behavior, affecting its practical applications in green chemistry and durable industries.
FAQs
1. What is HCOOCH?
HCOOCH, or methyl formate, is an organic compound used as a solvent and intermediate in chemical synthesis.
2. What happens in the reaction of HCOOCH with CH₂ and H₂O?
The reaction forms more stable compounds through hydrolysis and addition, often producing formic acid and methanol.
3. What is the role of water (H₂O) in this reaction?
Water acts as a reactant, aiding in the hydrolysis of HCOOCH to break it into simpler molecules.
4. Where is this reaction commonly used?
This reaction is used in organic chemistry labs, industrial synthesis, and sometimes in astrochemical studies.
5. Is the HCOOCH + CH₂ + H₂O reaction safe?
With proper lab precautions, it is safe. However, HCOOCH is flammable and should be handled carefully.
For more insightful chemistry content, visit Creative Stream and explore the world of molecules with us.